Concrete additives can help to enhance concrete properties while simultaneously cutting costs. Plasticizers increase workability by decreasing water content requirements; pumping aids increase pumpability; thickeners thicken paste for greater pumpability; while air entraining agents entangle air bubbles within concrete to minimize freeze-thaw damage while increasing strength.
Strength
Concrete is an extremely strong and long-lasting material, capable of withstanding various forces and stresses. It is often employed in structures which must withstand large loads or high stresses; concrete has the strength and resilience needed to withstand compressive, shear, flexural and thermal expansion/contraction forces.
Concrete stands out as both strong and environmentally-friendly material. It doesn’t release harmful toxins into the air or attract insects or rodents, plus its durability allows it to be reused for various applications.
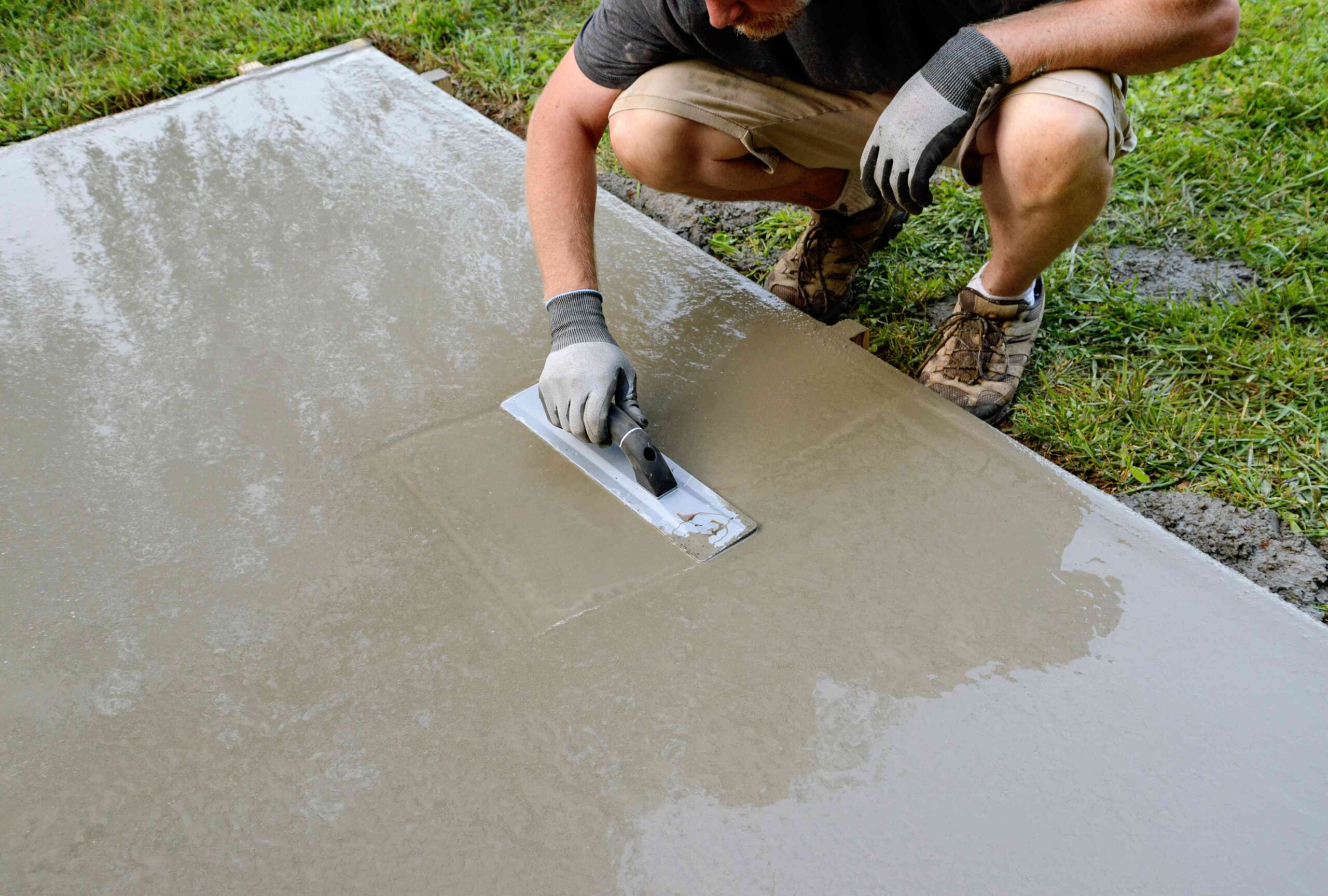
Concrete house slabs Melbourne is a durable construction material made of aggregates (small stones, gravel and sand), cement and water mixed together into an elastic mixture that can be formed into various shapes and sizes by hand or machinery in an industrial plant called a “concrete plant”.
Concrete is an incredibly versatile material that can be tailored to suit a wide range of needs, from infrastructure construction projects to providing access for disabled persons. Concrete mixes may include various aggregates, cements and chemical additives such as fly ash. Fly ash may be added as reinforcement material to increase strength while decreasing energy costs while high range water reducers may help enhance its workability.
Durability
Concrete’s durability makes it an appealing building material. It can withstand natural disasters such as hurricanes and tornadoes, while remaining fireproof. Furthermore, it offers good sound insulation qualities and can withstand heavy loads without crumbling under pressure – not only that but its cost-effective nature makes it suitable for multiple projects.
Concrete is also eco-friendly. Producing it requires less energy than other materials and it can be recycled after its lifespan has expired. Furthermore, its insulation properties keep buildings cool during summer and warm during winter – potentially cutting operational energy costs by as much as 8%!
Cement is the main component of concrete, along with sand, gravel and crushed stone (fine and coarse aggregates). To produce more sustainable mixes, air entraining agents may be added to reduce damage during freeze-thaw cycles while increasing strength. Recycled aggregates such as slag or bottom ash may also be utilized.
Flexibility
Concrete is an extremely versatile building material, able to be formed into many different shapes while still in liquid state. This makes it popular for crafting garden and home ornaments such as water fountains, gnomes and pillars – structures which can then be colored using pigments for an eye-catching finish that complements any building project beautifully.
Concrete stands up better to natural disasters than wood; therefore it makes an excellent material choice for use in buildings and bridges. Concrete has the strength to withstand hurricane-force winds as well as severe weather conditions while remaining fireproof.
Another advantage of concrete construction is its minimal need for repairs or maintenance. It is designed to last twice as long as wood, while becoming stronger over time. Furthermore, its sustainability benefits such as soundproofing and energy efficiency make it a good choice for green construction; additionally, local materials make concrete production much less polluting.
Cost
Concrete is a widely-used building material, often employed in the foundations and driveways of homes and driveways as well as to erect the skeletons of buildings – such as columns and beams – of buildings. Furthermore, it serves as an eco-friendly green material which is durable yet insulating; manufactured from recycled materials it reduces environmental pollution; its insulation keeps heat inside buildings for reduced energy use and lower environmental impact while helping combat smog by binding with pollutants such as nitric oxides.
Concrete can be constructed from various aggregate materials, including recycled glass and metals. Molding concrete to fit desired structures reduces waste while also helping builders use less material overall. Plus, its minimal maintenance requirements extend its life indefinitely while it resists water and fungi damage; additionally it can even be poured during cold weather without risk of cracking or breaking!